P1W2: Dwindling Water
backUnderstand /5
P1.2.1 Seven Days, Seven Ways
Testing water
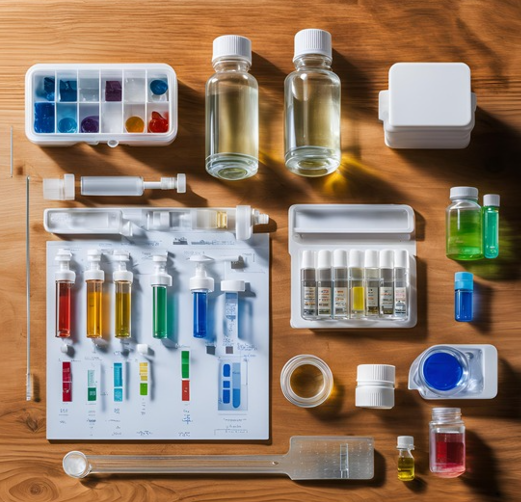 |
- | A water test kit can measure various properties of water to check its quality and detect pollutants. |
This super kit measures...
| pH 🌡️ | How acidic or alkaline the water is (scale 0–14). Neutral water has a pH of 7. Lemon 🍋 has a pH of 2, it is acidic. If water has lower or higher pH than 7, then it has something not good in it. |
| Turbidity 🌫️ | Checks how clear or cloudy the water is, often caused by dirt, algae, or pollutants. |
| Chlorine Levels 🧪 | Found in treated water, too much can cause a strong taste or irritation. |
| Nitrates and Nitrites 🌱 |
Often from fertilizers, these can harm health, especially for babies. Good water source doesn't have any of them. |
| Phosphates 🧴 |
From detergents or fertilizers, they cause algae overgrowth in water. |
| Hardness 🪨 |
Measures minerals like calcium and magnesium that can make water "hard." |
| Metals 🛢️ |
Tests for lead, mercury, arsenic, or iron, which can be harmful to health. Very harmful... |
| Pesticides 🚜 |
Detects chemicals from farming that can pollute water. |
| Oil or Grease 🛢️ |
Industrial pollution or spills. |
| Bacteria 🦠 |
Detects harmful bacteria like E. coli that can cause diseases. |
Take some water from different sources and play your detective game. If you don't have a super test kit, never mind, you can still obesrve these things:
- Does the water look clear or cloudy? 🌫️
- Describe what you see. Cloudy water might mean dirt, algae, or pollutants.
- Does the water have a smell? 👃
- Does it smell fresh, like chlorine, or if it has a bad odor (e.g., rotten eggs for sulfur)?
- What is the water’s temperature? 🌡️
- Use your hands to compare the water to the air. Is it too hot, too cold, or just right?
- Does the water leave stains or spots? 🪨
- Look at dried watermarks on glasses. White marks may mean "hard" water with lots of minerals.
- What happens when you squeeze a lemon into water? 🍋
- Check pH without measuring: lemon juice makes water more acidic (you can taste or smell the change).
- Does soap lather easily in the water? 🫧
- Hard water makes it harder for soap to foam, while soft water foams easily.
- Are there visible particles or debris in the water? 🗑️
- Look for dirt, algae, or trash floating in or settled at the bottom of water.
- Are there oil or rainbow-like patches on puddles? 🛢️
- How this could indicate pollution from vehicles or factories?
- What’s around the water source? 🌍
- Are there farms, factories, or garbage nearby? How these can affect water quality?
- What happens if you leave water in a jar for a few days? ⏳
- Observe if anything grows (e.g., algae) or settles at the bottom of your water sample. This can lead to the presence of bacteria and dirt in stagnant water.
